
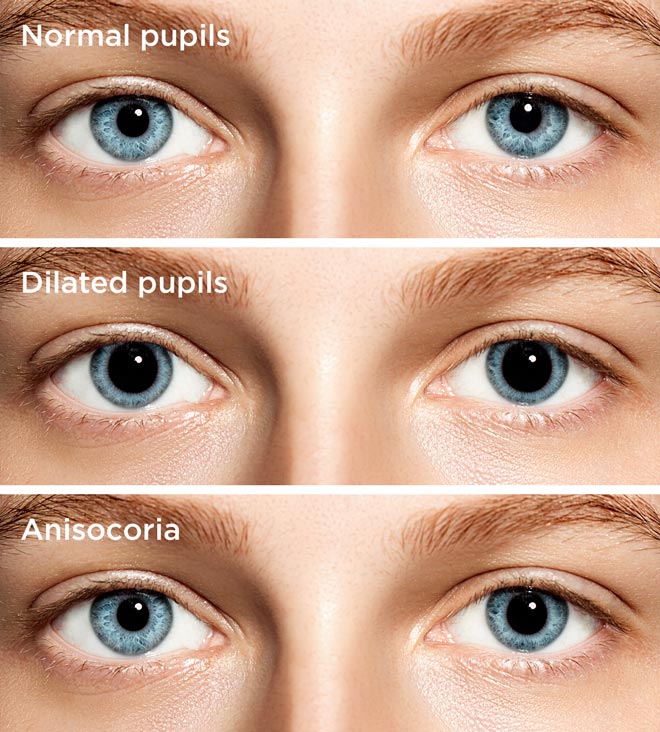
Two very common retinal diseases, diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration (AMD), are diagnosed and monitored by examining the retina through a dilated pupil. Learn about what to expect during a glaucoma eye exam. This is important for the diagnosis of glaucoma, as well as other diseases of the optic nerve. The optic nerve can be seen through an undilated pupil, but for optimum viewing a dilated pupil is required. What Conditions are Diagnosed with a Dilated Eye Exam? While in the past there were some eye drops that could reverse the dilation, these are no longer available, so you will have to wait the 4-6 hours before the drops completely wear off. If it is your first time having your eyes dilated or you know your vision is too impaired for driving after dilation, bring a friend or companion to drive you home from your examination. Some patients feel a “tightening” or different sensation in their eyelids. You may also experience blurry vision, particularly if you are trying to read. Once your eyes are dilated, there is an increase in light sensitivity because the pupil is large and more light is coming through, so bring your sunglasses, or your ophthalmologist may provide some disposable shades for your use. Some individuals may experience eye dilation that lasts longer. When eyes are dilated during an eye exam, it typically takes 4-6 hours for pupils to return to normal. Once the drops are administered, it typically takes 15-30 minutes to achieve fully dilated pupils, depending on the person’s response to the medication. How Long Does it Take for the Eyes to Fully Dilate? This is achieved through the use of eye drops. In order to see the entire retina, the pupil must be dilated. When your pupil is small, an eye doctor can see your optic nerve and macula but the view is limited. The view to the back of the eye is limited when the pupil is not dilated.
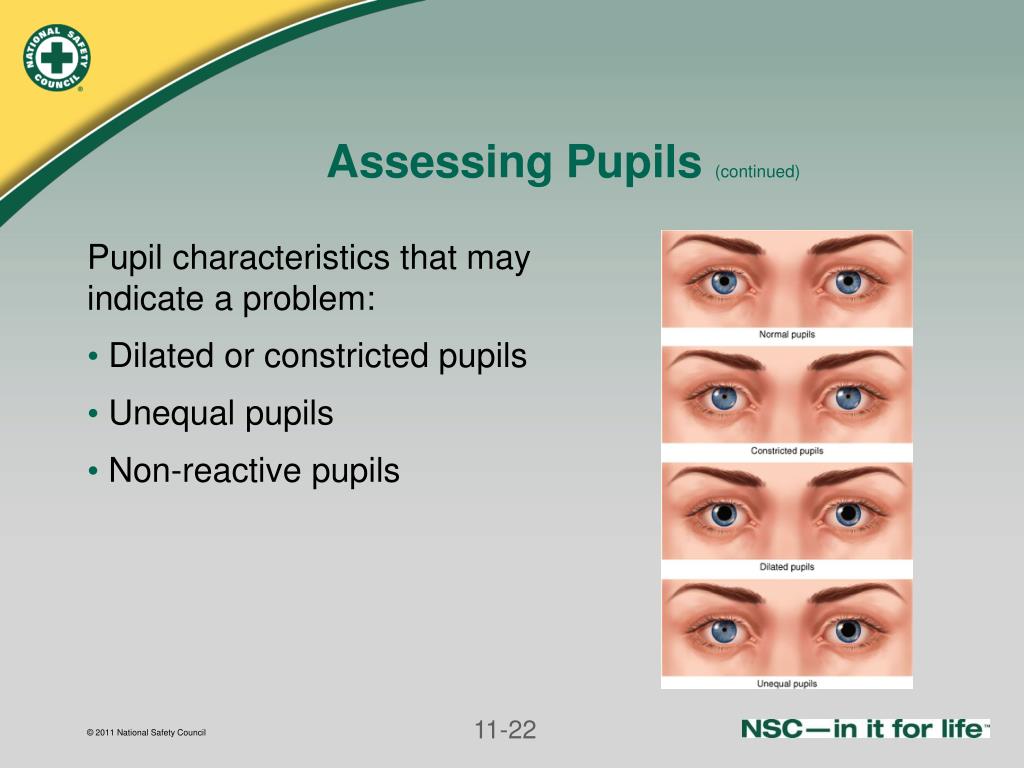
Ideally, your eyes are not dilated during this test.įinally, there are other parts of the front of the eye, the iris for example, which should be examined when your eyes are not dilated. Part of a glaucoma examination is formal visual field testing, where your peripheral, or side vision, is tested. When the angle is narrow, only portions of the drainage angle are visible, and in acute angle-closure glaucoma, none of it is visible. When the angle is open, your ophthalmologist can see most, if not all, of your eye’s drainage system. The “angle” that is being referred to is the angle between the iris, which makes up the colored part of your eye, and the cornea, which is the clear window front part of your eye. There is also an examination, called gonioscopy, which allows the doctor to examine your eye’s drainage angle with a special mirrored lens. This can be important for determining whether the visual pathways for each eye are functioning properly. In addition, eye doctors will examine your pupils’ responses to light prior to dilation. One of the first parts of a comprehensive eye exam is a test of your vision, and perhaps a measurement to determine an eyeglass prescription, both of which require that your eyes remain undilated. The observation of that nerve is a crucial part of a comprehensive eye examination.”īoth the dilated and the undilated eye exams provide important information to an eye doctor. The eye is a beautiful organ, and it is the only place in the human body where a doctor can see a part of the central nervous system, the optic nerve. During an eye exam, a doctor will administer eye drops to increase the size of a patient’s pupils. Under normal circumstances, pupils can dilate to let in more light or in response to a variety of stimuli. Pupil dilation occurs when the opening in the center of your iris grows bigger to let in more light. The exam is critical to preventing and treating eye conditions that could potentially lead to vision loss. Pupil dilation is performed to purposefully increase the size of the pupils during an eye exam so that the eye doctor can fully examine the health of the optic nerve and retina.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
